Critical Infrastructure Under Siege: Chinese Espionage, SVG-Based Phishing, Ransomware Surge, and Zero-Day Exploits Target Global Networks
In our latest Cyber Intelligence Brief, Deepwatch ATI looks at new threats and techniques to deliver actionable intelligence for SecOps organizations.
Each week we look at in-house and industry threat intelligence and provide ATI analysis and perspective to shine a light on a spectrum of cyber threats.
Contents
- Salt Typhoon: Chinese Campaigns Against Global Networks
- The SVG Threat: Phishing & Covert Malware Delivery
- Ransomware Activity Bulletin: Ransomware and Data Extortion Trends (August 26 -September 1)
- Exploited Vulnerabilities in TP-Link, WhatsApp, and Sangoma FreePBX Added to CISA’s Catalog – Immediate Mitigation Recommended
Salt Typhoon: Chinese Campaigns Against Global Networks
The Rundown
Since at least 2021, the China-backed hacking group known as Salt Typhoon (also tracked as OPERATOR PANDA, RedMike, UNC5807, and GhostEmperor) has conducted extensive global hacking campaigns targeting critical infrastructure, including telecommunications, government, transportation, lodging, and military networks worldwide. In the United States, major phone and internet providers such as AT&T, Verizon, and Lumen have been compromised, with T-Mobile also targeted. This group gains initial access primarily by exploiting publicly known and already patched vulnerabilities on network edge devices, rather than relying on zero-days. Notable exploited vulnerabilities include those in Ivanti Connect Secure (CVE-2024-21887), Palo Alto PAN-OS GlobalProtect (CVE-2024-3400), and various Cisco IOS XE software flaws (CVE-2023-20273, CVE-2023-20198, CVE-2018-0171). Once inside, these actors leverage custom SFTP clients and malware like JumbledPath, modifying network configurations, establishing tunnels, and abusing features like Cisco Guest Shell containers to maintain persistent access and evade detection.
The primary impact of these intrusions is the access and exfiltration of sensitive information, supporting a wide-ranging espionage operation believed to be directed by China’s Ministry of State Security and the People’s Liberation Army. The hackers have been observed accessing real-time unencrypted calls and text messages, alongside metadata, from U.S. telecom networks. They also acquire subscriber details, customer records, network diagrams, device configurations, administrator credentials, and even U.S. law enforcement wiretap systems. This stolen data provides Chinese intelligence services with the capability to identify and track the communications and movements of high-value targets globally, including U.S. officials, senior Americans, and presidential candidates. Techniques for persistence and evasion are sophisticated, involving the modification of Access Control Lists (ACLs), opening non-standard ports for SSH and HTTP, creating Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE)/IPsec tunnels, redirecting TACACS+ servers to capture authentication traffic, and clearing logs.
For organizations, this threat underscores a critical vulnerability: the continued successful exploitation of known and patched flaws, indicating a gap in fundamental cybersecurity hygiene rather than zero-day defense. Organizations are strongly urged to prioritize the immediate patching of all known exploited vulnerabilities, especially on internet-exposed edge devices. A robust security posture necessitates hardening device configurations, strictly enforcing secure management protocols (e.g., SSHv2, SNMPv3, HTTPS), and disabling all unnecessary services, particularly legacy features like Cisco Smart Install and Guest Shell where not operationally required. Furthermore, comprehensive logging and vigilant monitoring for unauthorized configuration changes, anomalous network services, tunnel creation, and container activity are essential for early detection and full eviction. Implementing management-plane isolation, robust change management processes, and adopting end-to-end encrypted messaging applications for sensitive communications are also critical proactive measures against this persistent espionage threat.
Source Material: Joint Advisory
The SVG Threat: Phishing & Covert Malware Delivery
The Rundown
The central theme across the sophisticated use of Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) files as a potent attack vector. Threat actors are weaponizing these seemingly harmless XML-based image files by embedding malicious JavaScript, often concealed through multi-layered obfuscation techniques such as Base64 encoding within <foreignObject> or <iframe> tags, string reversal, junk character insertion, and polymorphism. This technique, dubbed “Script in the Shadows” by Intezer, is alarmingly effective because it allows the malicious code to evade traditional antivirus engines and email security filters, frequently achieving “zero detections” on platforms like VirusTotal. The inherent ability of SVG files to house scripts and interactive elements transforms them from innocuous images into tools for covert operations.
This evasive method has been actively exploited in a specific campaign primarily targeting the Colombian judicial system, impersonating the Fiscalía General de la Nación. In these attacks, the hidden JavaScript within the SVG files decodes and injects fake login pages designed for credential harvesting. Simultaneously, while displaying a deceptive “file download” progress bar, the SVG acts as a malware dropper, secretly delivering additional payloads like malicious ZIP archives in the background. VirusTotal’s Code Insight tool was crucial in uncovering this campaign, revealing 44 unique malicious SVG files that had previously gone undetected, leading to the identification of 523 samples dating back to August 2025. This highlights the critical need for advanced, format-aware inspection mechanisms to combat these evolving threats that bypass conventional security measures.
Source Material: VirusTotal, Intezer
Ransomware Activity Bulletin: Ransomware and Data Extortion Trends (August 26 -September 1)
The Rundown
Between August 26 through September 1, ransomware and data extortion incidents impacted 100 organizations across 18 leak sites, marking an approximate 5.26% increase from the previous week’s total of 95. While this uptick could suggest heightened ransomware activity, it more likely reflects a short-term surge in threat actor operations rather than a sustained escalation in attack frequency.
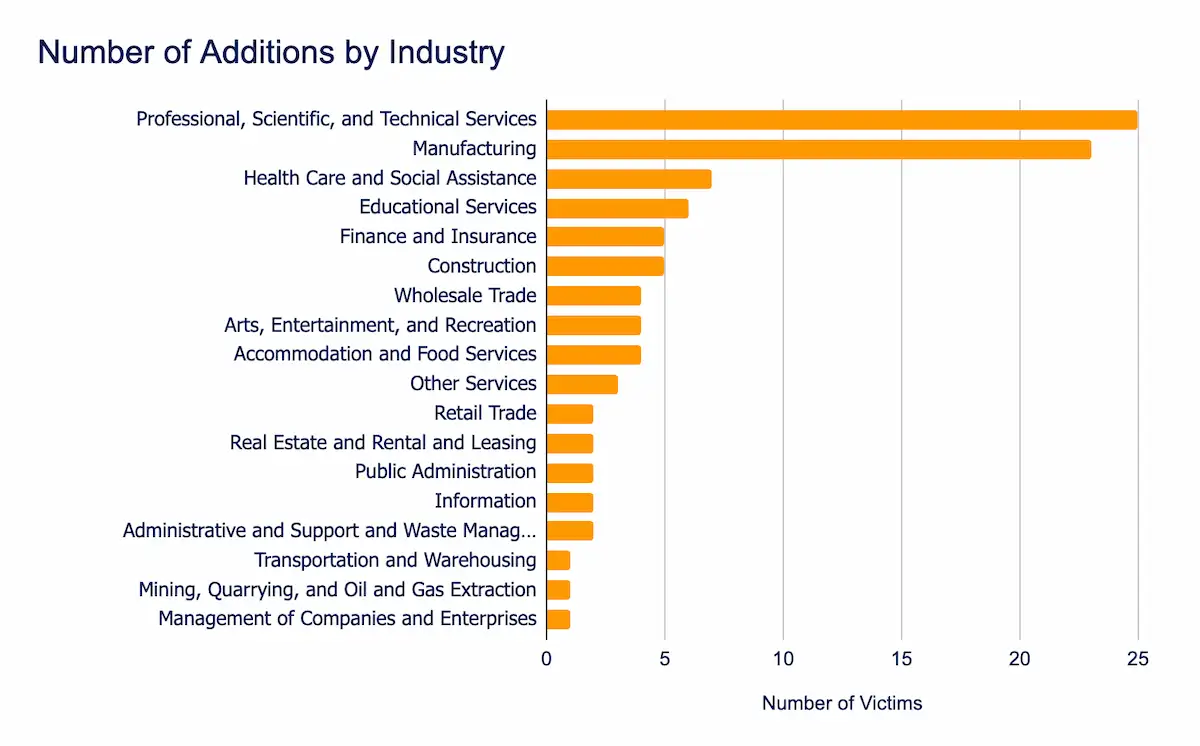
Professional, Scientific, and Technical Services, Manufacturing, Healthcare and Social Assistance sectors remained the most heavily targeted, underscoring the continued focus on high-value, disruption-prone industries. Geographically, the United States, Canada and United Kingdom saw the highest number of incidents, reinforcing threat actors’ concentration on strategically significant markets.
For business leaders, these patterns highlight the calculated and persistent nature of ransomware campaigns. Despite periodic shifts in weekly volume, the overall threat landscape remains volatile, emphasizing the importance of sustained investment in comprehensive prevention, detection, and incident response capabilities.
Key Trends:
- Most affected industries:
- Professional, Scientific, and Technical Services
- Manufacturing
- Healthcare and Social Assistance
- Most affected countries:
- United States
- Canada
- United Kingdom
- Most active leak sites:
- Safeplay
- Crypto24
- Qilin
Exploited Vulnerabilities in TP-Link, WhatsApp, and Sangoma FreePBX Added to CISA’s Catalog – Immediate Mitigation Recommended
The Rundown
Between August 28 through September 3, CISA added 5 critical vulnerabilities to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, affecting TP-Link hardware and products, WhatsApp, and Sangoma FreePBX. These flaws have been confirmed as actively exploited in diverse threat campaigns.
If left unpatched, the vulnerabilities pose severe risks, including unauthorized access and privilege escalation, jeopardizing the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of impacted systems. Successful exploitation could lead to significant operational disruptions, data compromise, and lasting reputational damage.
Given the growing interest from both nation-state actors and financially motivated threat groups, immediate remediation is imperative. Delayed action substantially increases the likelihood of compromise and could trigger cascading impacts across interconnected IT and operational environments.
TP-Link | Multiple Routers CVE-2025-9377
- Vulnerability Description: TP-Link Archer C7(EU) and TL-WR841N/ND(MS) contain an OS command injection vulnerability that exists in the Parental Control page. The impacted products could be end-of-life (EoL) and/or end-of-service (EoS). Users should discontinue product utilization.
- Exploited in a Ransomware attack? Unknown
- Action: Apply updates per vendor instructions.
- Date Added to catalog: 2025-09-03
- Recommended Mitigation Due Date: 2025-09-24
TP-Link | TL-WR841N CVE-2023-50224
- Vulnerability Description: TP-Link TL-WR841N contains an authentication bypass by spoofing vulnerability within the httpd service, which listens on TCP port 80 by default, leading to the disclose of stored credentials. The impacted products could be end-of-life (EoL) and/or end-of-service (EoS). Users should discontinue product utilization.
- Exploited in a Ransomware attack? Unknown
- Action: Apply updates per vendor instructions.
- Date Added to catalog: 2025-09-03
- Recommended Mitigation Due Date: 2025-09-24
Meta Platforms | WhatsApp CVE-2025-55177
- Vulnerability Description: Meta Platforms WhatsApp contains an incorrect authorization vulnerability due to an incomplete authorization of linked device synchronization messages. This vulnerability could allow an unrelated user to trigger processing of content from an arbitrary URL on a target’s device.
- Exploited in a Ransomware attack? Unknown
- Action: Apply updates per vendor instructions.
- Date Added to catalog: 2025-09-02
- Recommended Mitigation Due Date: 2025-09-23
TP-Link | TL-WA855RE CVE-2020-24363
- Vulnerability Description: TP-link TL-WA855RE contains a missing authentication for critical function vulnerability. This vulnerability could allow an unauthenticated attacker (on the same network) to submit a TDDP_RESET POST request for a factory reset and reboot. The attacker can then obtain incorrect access control by setting a new administrative password. The impacted products could be end-of-life (EoL) and/or end-of-service (EoS). Users should discontinue product utilization.
- Exploited in a Ransomware attack? Unknown
- Action: Apply updates per vendor instructions.
- Date Added to catalog: 2025-09-02
- Recommended Mitigation Due Date: 2025-09-23
Sangoma | FreePBX CVE-2025-57819
- Vulnerability Description: Sangoma FreePBX authentication bypass vulnerability contains an authentication bypass vulnerability due to insufficiently sanitized user-supplied data allows unauthenticated access to FreePBX Administrator leading to arbitrary database manipulation and remote code execution.
- Exploited in a Ransomware attack? Unknown
- Action: Apply updates per vendor instructions.
- Date Added to catalog: 2025-08-29
Recommended Mitigation Due Date: 2025-09-19
Source Material: CISA
Share