Cloud Account Takeovers, Emerging Botnets, and Exploited Vulnerabilities: AWS Campaign and NightshadeC2 Mark a Shift in Threat Actor Tactics
In our latest Cyber Intelligence Brief, Deepwatch ATI looks at new threats and techniques to deliver actionable intelligence for SecOps organizations.
Each week we look at in-house and industry threat intelligence and provide ATI analysis and perspective to shine a light on a spectrum of cyber threats.
AWS Cloud Email Takeover Campaign
The Rundown
The impact of this campaign is multifaceted, carrying significant risks for victims and highlighting critical vulnerabilities in cloud security. Primarily, the attackers used compromised AWS access keys to launch a large-scale phishing operation from trusted domains, leveraging Amazon SES’s production mode. This allowed malicious traffic to blend seamlessly with legitimate email flows, bypassing traditional defenses and shifting financial costs and reputational damage onto the victim. The phishing messages referenced “2024 tax forms” and linked to a credential theft site, with the primary objective assessed as financial gain through credential theft, business email compromise, and other schemes.
Beyond the direct financial and data theft risks, SES abuse carries broader implications. If attackers can send emails from a victim’s verified domains, it leads to brand damage and enables spearphishing and fraud. It also serves as a clear indicator of compromised risk, showing that adversaries already control valid AWS credential, which could be used for more impactful actions beyond email abuse. Furthermore, such activity can trigger abuse complaints to AWS, potentially resulting in an abuse case being filed against the victim’s account, posing an operational risk. The campaign also introduced novel techniques, such as multi-regional PutAccountDetails requests, which were previously undocumented in SES abuse, offering new insights into attacker tradecraft.
Source Material: Wiz
Newly Discovered NightshadeC2 Botnet
The Rundown
NightshadeC2, a recently identified botnet and infostealer, poses a significant and multi-faceted threat to organizations. This malware enables comprehensive system control, including keystroke and clipboard monitoring, reverse shell access, and the execution of additional payloads. Crucially, it facilitates the theft of sensitive credentials, such as browser passwords and cookies, from victim systems. Initial compromise frequently occurs via deceptive ClickFix campaigns that leverage booking[.]com-themed pages or through trojanized legitimate software, exposing organizations to data exfiltration and unauthorized system manipulation.
NightshadeC2 leverages both C and Python-based variants communicating with unidentified Command and Control (C2) frameworks. A key adversary tactic involves “UAC Prompt Bombing,” a technique designed to bypass malware analysis sandboxes and force users into granting Windows Defender exclusions, thereby facilitating payload delivery and evasion. Adversaries further leverage existing User Account Control (UAC) bypasses to escalate privileges, demonstrating persistent efforts to overcome security controls. The malware’s extensive capabilities also include remote control, screen capturing, and the ability to launch hidden web browsers.
Source Material: eSentire
Ransomware and Data Extortion Trends (September 2 – 8)
The Rundown
Between September 1 through September 8, ransomware and data extortion incidents impacted 85 organizations across 20 leak sites, marking an approximate 15% decrease from the previous week’s total of 100. While this uptick could suggest heightened ransomware activity, it more likely reflects a short-term surge in threat actor operations rather than a sustained escalation in attack frequency.
Manufacturing, Professional Services, and Healthcare and Social Assistance sectors remained the most heavily targeted, underscoring the continued focus on high-value, disruption-prone industries. Geographically, the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom saw the highest number of incidents, reinforcing threat actors’ concentration on strategically significant markets.
For business leaders, these patterns highlight the calculated and persistent nature of ransomware campaigns. Despite periodic shifts in weekly volume, the overall threat landscape remains volatile, emphasizing the importance of sustained investment in comprehensive prevention, detection, and incident response capabilities.
Key Trends:
- Most affected industries:
- Manufacturing
- Professional, Scientific, and Technical Services
- Healthcare and Social Assistance
- Most affected countries:
- United States
- Canada
- United Kingdom
- Most active leak sites:
- Lynx
- Akira
- Qilin
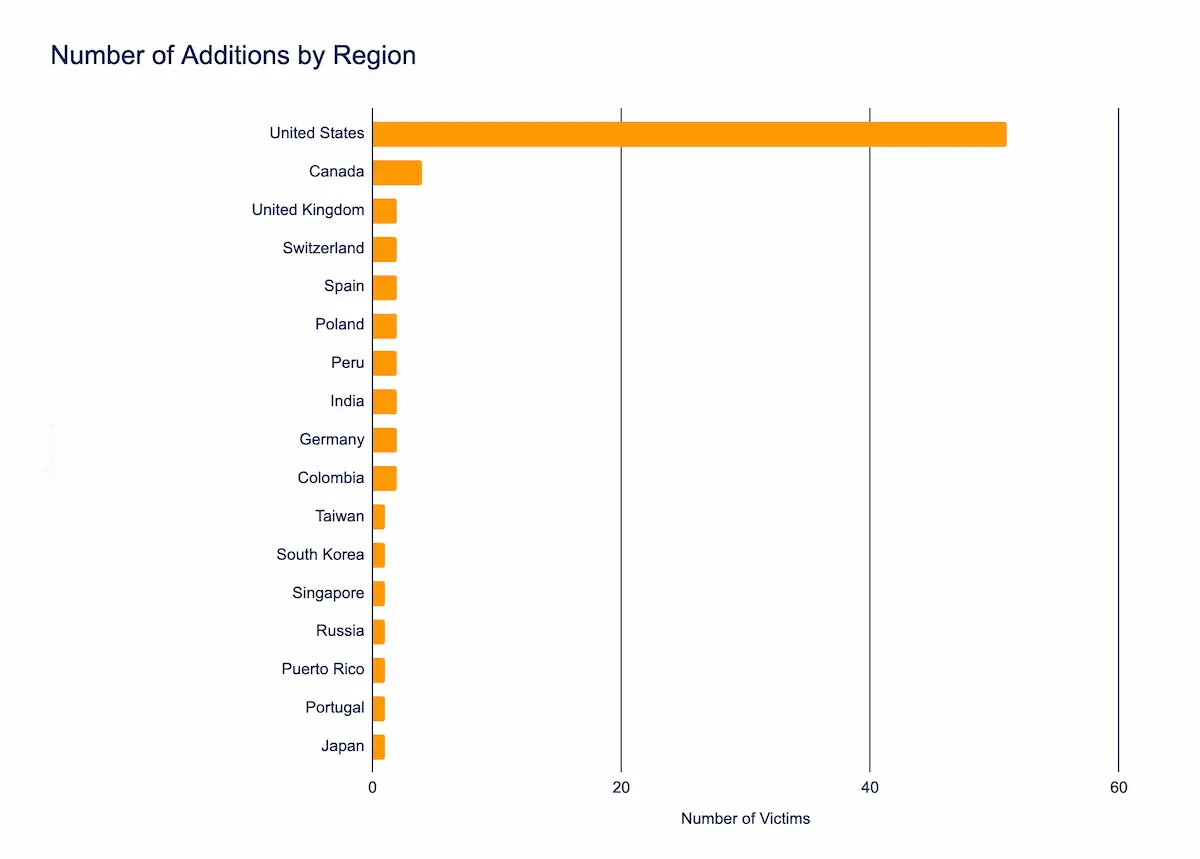
Exploited Vulnerabilities in Sitecore, Android, and Linux Added to CISA’s Catalog
The Rundown
Between September 4 through September 10, CISA added 3 critical vulnerabilities to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, affecting Sitecore, Android, and Linux. These flaws have been confirmed as actively exploited in diverse threat campaigns.
If left unpatched, the vulnerabilities pose severe risks, including unauthorized access and privilege escalation, jeopardizing the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of impacted systems. Successful exploitation could lead to significant operational disruptions, data compromise, and lasting reputational damage.
Given the growing interest from both nation-state actors and financially motivated threat groups, immediate remediation is imperative. Delayed action substantially increases the likelihood of compromise and could trigger cascading impacts across interconnected IT and operational environments.
Sitecore | Multiple Products CVE-2025-53690
- Vulnerability Description: Sitecore Experience Manager (XM), Experience Platform (XP), Experience Commerce (XC), and Managed Cloud contain a deserialization of untrusted data vulnerability involving the use of default machine keys. This flaw allows attackers to exploit exposed ASP.NET machine keys to achieve remote code execution.
- Exploited in a Ransomware attack? Unknown
- Action: Apply updates per vendor instructions.
- Date Added to catalog: 2025-09-04
- Recommended Mitigation Due Date: 2025-09-25
Android | Runtime CVE-2025-48543
- Vulnerability Description: Android Runtime contains a use-after-free vulnerability, potentially allowing a Chrome sandbox escape leading to local privilege escalation.
- Exploited in a Ransomware attack? Unknown
- Action: Apply updates per vendor instructions.
- Date Added to catalog: 2025-09-04
- Recommended Mitigation Due Date: 2025-09-25
Linux | Kernel CVE-2025-38352
- Vulnerability Description: Linux kernel contains a time-of-check time-of-use (TOCTOU) race condition vulnerability that has a high impact on confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
- Exploited in a Ransomware attack? Unknown
- Action: Apply updates per vendor instructions.
- Date Added to catalog: 2025-09-04
- Recommended Mitigation Due Date: 2025-09-25
Recommendations
ATI recommends mitigative action occur according to the mitigation “Due Date” recommended by CISA.
Source Material: CISA
Share