When Invites Become Threats: iCloud Calendar Lures, Salesforce Exploits, and Ransomware Actors Leverage Human Error and App Integrations.
In our latest Cyber Intelligence Brief, Deepwatch ATI looks at new threats and techniques to deliver actionable intelligence for SecOps organizations.
Each week, we look at in-house and industry threat intelligence and provide ATI analysis and perspective to shine a light on a spectrum of cyber threats.
Contents
When Invites Attack: How iCloud Calendar Delivers Social Engineering Lures
The Rundown
Threat actors are abusing Apple’s iCloud Calendar invite feature to send phishing messages that look like legitimate emails from Apple servers. In the attacks, the bad actors embed fraudulent “receipt” or “billing” notifications, often referencing services like PayPal, inside calendar invites. These invites are sent from a genuine Apple email address ([email protected]), and because they originate from Apple’s infrastructure, they often pass standard email authentication checks like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. That lets them bypass many spam filters. Once the recipient opens the invite, the phishing lure is typically a callback request, like asking them to call a fake support line, or to download remote access tools under the guise of correcting fraud.
This tactic blurs the lines between legitimate and malicious communication, increasing the risk that employees or customers will trust these messages. Since they pass authentication and come from what appears to be a trusted sender, they’re harder to block or spot with automated defenses. For companies, this raises exposure to social engineering attacks, potential credential theft, malware installation, or even wider network compromise if remote access tools are misused. It underscores the need for robust user training (to treat unexpected calendar invites with suspicion), enhanced monitoring of inbound calendar traffic, and careful configuration of email and calendar policies to limit abuse.
Source Material: Bleeping Computer
FBI Warns of Targeted Salesforce Attacks Exploiting Human Error and App Integrations
The Rundown
The FBI has issued a warning that cybercriminal groups are specifically targeting Salesforce, a platform many companies use to manage customers and sales. These attackers use two main strategies: one involves calling support staff and tricking them into granting access, while the other takes advantage of trusted third-party apps that are already connected to Salesforce. In both cases, the goal is to steal large amounts of company and customer data, which can then be used for extortion or sold to other criminals.
What makes these attacks especially concerning is that they exploit everyday business processes. Employees answering phones or approving apps may not realize they are being manipulated, and integrations with legitimate software can create hidden entry points. Because the attackers are using authorized connections, traditional security alerts may not trigger, allowing the theft to go unnoticed until it’s too late. The end result is potential data loss, reputational harm, and costly recovery efforts.
To counter this threat, companies are urged to act now. Training staff to recognize scams, especially in customer service roles, is critical. Stronger multi-factor authentication and tighter control of third-party app access can block many attempts. Businesses should also review their Salesforce integrations regularly, monitor for unusual activity, and prepare clear response plans in case of an incident. Taking these steps not only protects sensitive information but also helps maintain customer trust and business continuity.
Source Material: FBI Flash
Ransomware and Data Extortion Trends (September 9 – 15)
The Rundown
Between September 9 and 15, ransomware and data extortion incidents impacted 127 organizations across 23 leak sites, representing a 49% increase from the previous week’s 85 cases. While this spike may indicate elevated activity, it more likely reflects a short-term surge in threat actor operations rather than a sustained escalation.
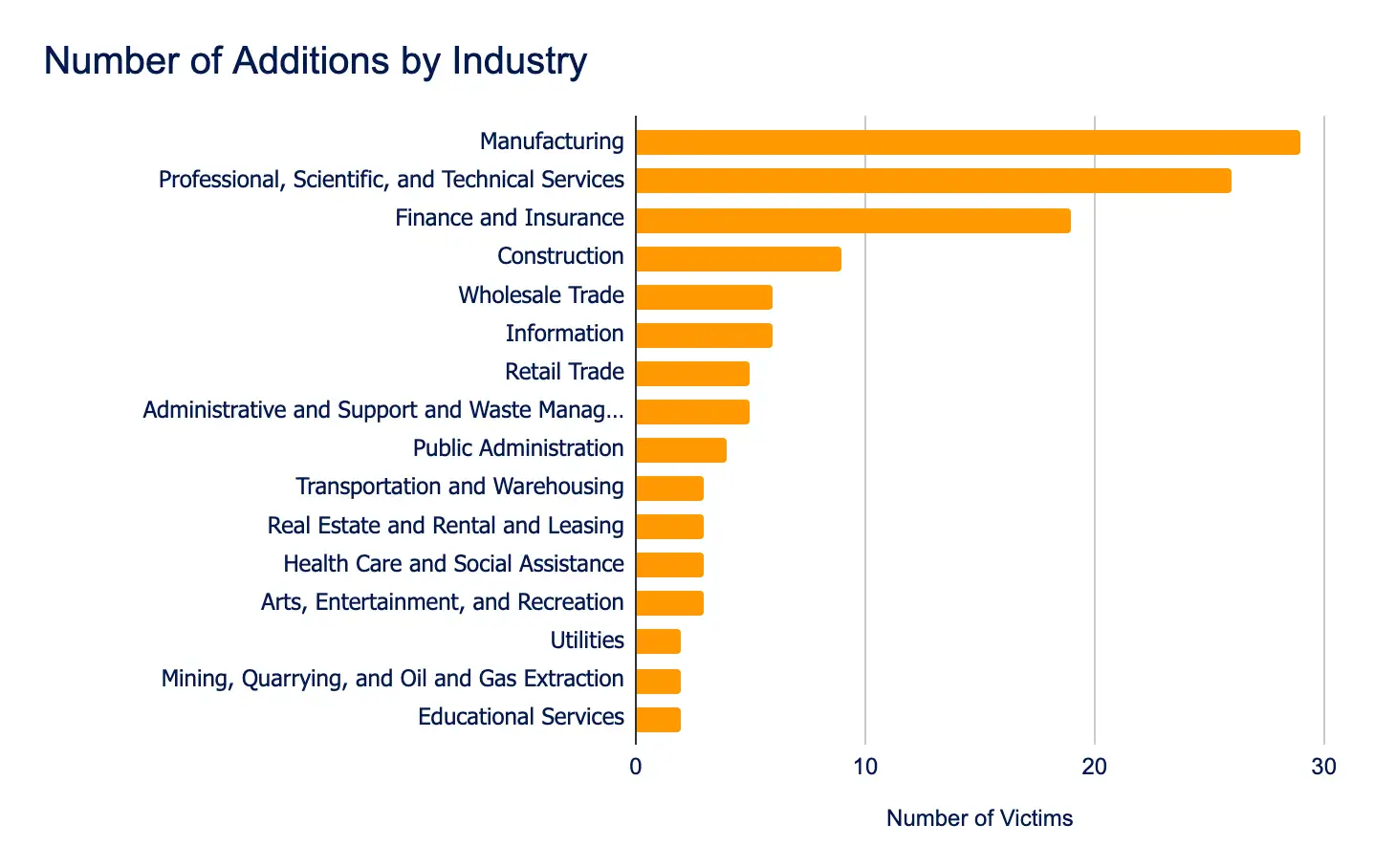
The Manufacturing, Professional Services, and Finance and Insurance sectors remained the most heavily targeted, highlighting continued focus on high-value, disruption-prone industries. Geographically, the United States, South Korea, Italy, France, and Canada experienced the highest concentration of incidents, underscoring threat actors’ prioritization of strategically significant markets.
For business leaders, these trends reinforce the calculated and persistent nature of ransomware campaigns and the need for sustained investment in comprehensive prevention, detection, and incident response capabilities.
Key Trends:
- Most affected industries:
- Manufacturing
- Professional, Scientific, and Technical Services
- Finance and Insurance
- Most affected countries:
- United States
- South Korea
- Italy
- France
- Canada
- Most active leak sites:
- Qilin
- Akira
- Play
Exploited Vulnerability in Dassault Systèmes Product Added to CISA’s Catalog
The Rundown
Between September 10 and 17, CISA added one critical vulnerability in a Dassault Systèmes product to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, confirming active exploitation across diverse threat campaigns. If left unpatched, the flaw could enable unauthorized access and privilege escalation, threatening the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of affected systems.
Successful exploitation may result in operational disruption, data compromise, and lasting reputational damage. With heightened interest from both nation-state actors and financially motivated groups, immediate remediation is imperative, as delayed action significantly increases the risk of compromise and cascading impacts across interconnected IT and operational environments.
Dassault Systèmes | DELMIA Apriso CVE-2025-5086
- Vulnerability Description: Dassault Systèmes DELMIA Apriso contains a deserialization of untrusted data vulnerability that could lead to a remote code execution.
- Exploitation Description: The vulnerability can be exploited remotely by sending specially crafted requests to the affected Dassault Systèmes product. Successful exploitation allows an attacker to bypass normal authentication controls and execute arbitrary code or escalate privileges within the compromised environment. Once initial access is established, threat actors can move laterally across the network, exfiltrate sensitive data, and disrupt core business functions.
- Exploited in a Ransomware attack? Unknown
- Action: Apply updates per vendor instructions
- Date Added to catalog: 2025-09-11
- Recommended Mitigation Due Date: 2025-10-02
Recommendations
ATI recommends mitigative action occur according to the mitigation “Due Date” recommended by CISA.
Source Material: CISA
Share