10.05.21 Deepwatch Labs Threat Report Update:
Recently Apache reported that the fix for CVE-2021-41773 in Apache HTTP Server 2.4.50 was deemed to be inadequate. As a result, a path traversal attack could map URLs to files outside the folders specified by Alias-like directives. This was given a new CVE identifier of CVE-2021-42013.
These requests may succeed if files outside of these directories are not protected by the default setting “require all refused.” If CGI scripts are enabled for these aliased patches, remote code execution may be possible.
Only Apache 2.4.49 and Apache 2.4.50 are affected; previous versions are unaffected.
The Deepwatch Threat Intel Team urges all customers that use Apache HTTP Servers running version 2.4.49 or 2.4.50 to upgrade to 2.4.51 immediately. At the time of this writing, neither Qualys, nor Rapid7, nor Tenable have the ability to scan for CVE-2021-42013.
Additionally, CVE-2021-41773 & CVE-2021-41524 are being tracked and scanned for by all three scanning providers, and the Vulnerability Management team is aware of these vulnerabilities and is monitoring for updates from the vendors.
Key Points:
- Active exploitation of Apache HTTP Server 2.4.49 has been observed, and proof-of-concept code is available. This vulnerability is tracked as CVE-2021-41773.
- If the exploitation is successful, threat actors can map URLs to files beyond the anticipated document root. Exploits of this weakness result in the source code of interpreted files, such as CGI scripts, being leaked.
- Apache has released a patch and urges organizations to upgrade to version 2.4.50 as soon as possible.
Summary:
The Apache Software Foundation has published a vulnerability advisory regarding HTTP Web Server version 2.4.49 to fix two vulnerabilities, CVE-2021-41773 & CVE-2021-41524. CVE-2021-41773 is a path traversal and file disclosure weakness that is being actively exploited and CVE-2021-41524 allows denial of service (DoS) attacks. These vulnerabilities only affect version 2.4.49, CVE-2021-41773 requires the “require all denied” access control parameter disabled, which appears to be the default configuration and CVE-2021-41524 requires a specially crafted request.
If CVE-2021-41773 is successfully exploited, threat actors can map URLs to files beyond the anticipated document root. Exploits of this weakness result in the source code of interpreted files, such as CGI scripts, being leaked. At this time no details of the active exploitation have been released.
CVE-2021-41524, a null pointer dereference discovered during HTTP/2 request processing. A threat actor can use this issue to cause a DoS attack on the server by using a specially crafted request, but this vulnerability is not known to be actively exploited at this time.
Deepwatch Threat Intelligence Outlook:
In a statement to BleepingComputer, Apache stated that “As Apache HTTP Server 2.4.49 was only released a few weeks ago, it’s likely many users will not have upgraded yet. If and how this issue can be exploited is highly dependent on how users will have configured the server. If you are using 2.4.49, it is recommended that you upgrade to the latest version instead of using access control configuration as a mitigation. On a default installation, an attacker could still use the flaw to obtain the source code of interpreted files like CGI scripts.”
The Threat Intel Team conducted a Shodan search and revealed that there are approximately 43,429 Apache HTTP Server running version 2.4.49 in the US and over 112,000 globally.
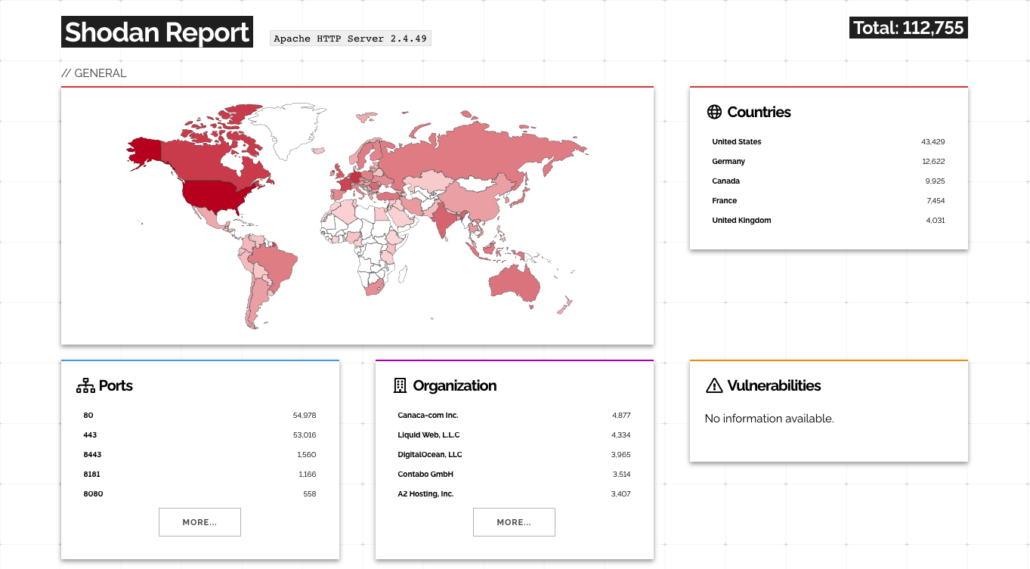
Deepwatch Threat Intel Team assesses with moderate confidence that exploitation of this vulnerability will continue in the near future due to the availability of proof-of-concept code and the abundance of vulnerable systems that have not been patched yet.
The Threat Intel Team recommends that all customers running Apache HTTP Server version 2.4.49 upgrade to version 2.4.50 as soon as possible. At the time of this writing, Qualys, Rapid7, nor Tenable have the ability to scan for these vulnerabilities. The Vulnerability Management team is aware of these vulnerabilities and is monitoring for updates from the vendors.
↑
Share