Published March 09, 2022
Prepared by Deepwatch Threat Intel Team
Key Points:
- Security researcher Max Kellermann disclosed a vulnerability that affects Linux Kernel versions 5.8 and later to include Android devices.
- The local privilege escalation vulnerability tracked as CVE-2022-0847, allows a non-privileged user to inject and overwrite data in read-only files, including SUID processes that run as root.
- In addition to publicly disclosing the vulnerability, Kellerman also published a proof-of-concept exploit code that was quickly followed up by improved exploit code from another researcher and publicly disclosed. The exploit code could allow a threat actor to inject their data into sensitive read-only files, eliminating restrictions or changing configurations to give them more access than they would have otherwise.
- Deepwatch Threat Intel Team assesses with moderate confidence that threat actors will incorporate the available exploits to compromise Linux systems. Furthermore, this vulnerability is particularly concerning for colleges and universities that frequently provide shell access to multi-user Linux systems. Therefore, the Deepwatch Threat Intel Team recommends that customers update their Linux kernels to 5.10.102, 5.15.25, or 5.16.11.
Summary
On March 7, security researcher Max Kellermann disclosed a local privilege escalation vulnerability that affects Linux Kernel versions 5.8 and later, including Android devices. The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2022-0847, allows a non-privileged user to inject and overwrite data in read-only files, including SUID processes that run as root.
In the disclosure, Kellerman stated that the limitations are:
- The threat actor must have read permissions.
- The offset must not be on a page boundary.
- The write cannot cross a page boundary.
- The file cannot be resized.
In addition to publicly disclosing the vulnerability, Kellerman also published a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code. The exploit code could allow a threat actor to inject their data into sensitive read-only files, eliminating restrictions or changing configurations to give them more access than they would have otherwise.
Shortly after the public disclosure, security researchers started testing the exploit code, with one researcher demonstrating its effectiveness by making sure the root user doesn’t have a password in the /etc/passwd file. After completing this change, a non-privileged user might simply use the ‘su root’ command to get root account access.
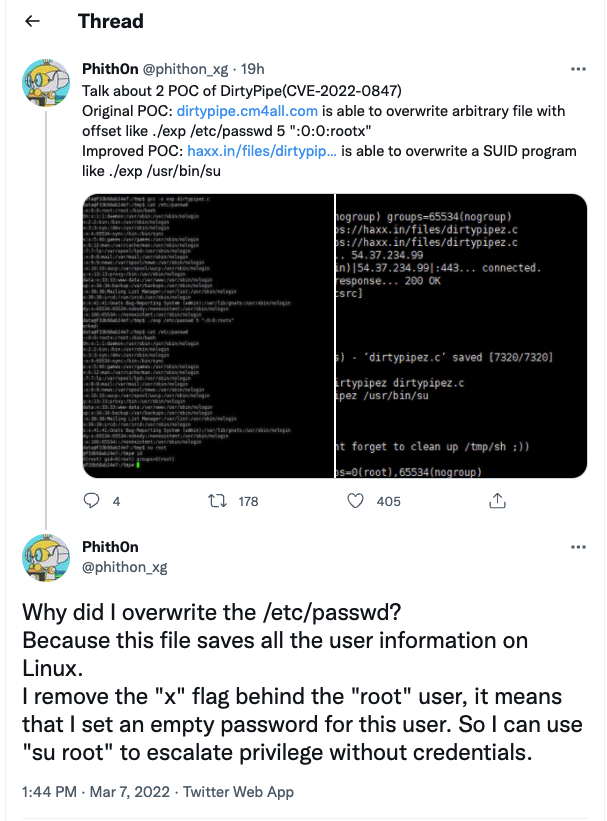
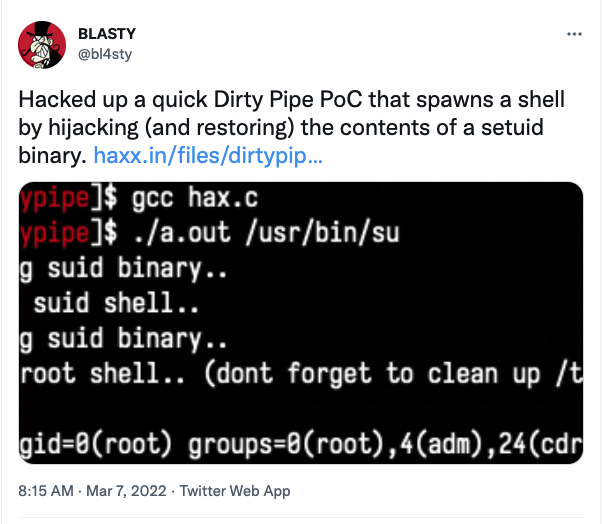
However, security researcher BLASTY disclosed an improved exploit that makes gaining root privileges easier by altering the /usr/bin/su command to dump a root shell at /tmp/sh and then executing the script02.
In their statements, they are extorting NVIDIA by threatening to release the 30 series hardware folder, “hw folder,” if NVIDIA does not “push an update for all 30 series firmware that remove lhr limitations.” Nvidia’s lite hash rate technology (LHR) allows graphics cards to minimize the mining capacity.
After executing the command, the user acquires root rights, as verified by BleepingComputer on Ubuntu 20.04.3 LTS running the 5.13.0-27-generic kernel.
Starting on February 20th, 2022, the vulnerability was responsibly disclosed to several Linux maintainers, including the Linux kernel security team and the Android Security Team.
Despite the vulnerability being resolved in Linux kernels 5.10.102, 5.15.25, or 5.16.11, many servers continue to use outdated kernels, making the release of this vulnerability a significant concern for server admins.
Tenable has released plugin ID 158682 to scan for this and other vulnerabilities listed in the dsa-5092 security advisory. At this time Qualys has not publicly disclosed any plugin IDs.
Deepwatch Threat Intelligence Outlook
Deepwatch Threat Intel Team assesses with moderate confidence that threat actors will incorporate the available exploits to compromise Linux systems. Furthermore, this vulnerability is particularly concerning for colleges and universities that frequently provide shell access to multi-user Linux systems. Therefore, the Deepwatch Threat Intel Team recommends that customers update their Linux systems as soon as an update is available for your specific version with the priority for the update going to systems that are internet-facing.
Author: Eric Ford
↑
Share