From Password Sprays to Persistent Threats: RansomHub Attacks, Iranian Cyber Ops, and Critical Vulnerabilities Target U.S. Interests
In our latest Cyber Intelligence Brief, Deepwatch ATI looks at new threats and techniques to deliver actionable intelligence for SecOps organizations.
Each week we look at in-house and industry threat intelligence and provide ATI analysis and perspective to shine a light on a spectrum of cyber threats.
Contents
From RDP to Ransom: How a Password Spray Led to a RansomHub Takeover
The Rundown
In November 2024, a threat actor executed a password spray attack against an exposed Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) server, attempting multiple logins over several hours. Upon successfully accessing the system, they employed tools like Mimikatz and Nirsoft’s CredentialsFileView to extract stored credentials and interact with LSASS memory. This enabled them to move laterally within the network, accessing domain controllers and other endpoints. They utilized legitimate administrative tools and conducted network discovery using utilities such as Advanced IP Scanner and NetScan.
The attackers exfiltrated data using Rclone, transferring it to a remote server via SFTP. Subsequently, they deployed RansomHub ransomware across the network. The ransomware propagated over SMB and was executed using remote services, leading to widespread encryption of systems.
This incident highlights the critical importance of securing RDP access and implementing robust credential management practices. Organizations should ensure that RDP services are not exposed to the internet without proper safeguards, enforce strong password policies, and monitor for unusual authentication patterns to prevent similar breaches.
Source Material: The DFIR Report
Beyond the Ceasefire: Ongoing Iranian Cyber Operations Against U.S. Interests
The Rundown
The joint fact sheet issued by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), FBI, NSA, and Department of Defense Cyber Crime Center (DC3) on June 30, 2025, warns U.S. businesses of heightened cyber threats from Iranian-affiliated actors. Despite a declared ceasefire between Iran and Israel, these actors, including state-sponsored groups and hacktivists, may continue to target U.S. critical infrastructure and entities, particularly those connected to Israeli research and defense firms. The advisory emphasizes the need for vigilance and proactive cybersecurity measures to mitigate potential disruptions and data breaches.
The fact sheet highlights that Iranian cyber actors exploit vulnerabilities such as unpatched software and default passwords to gain unauthorized access to networks and devices. They employ tactics like automated password guessing, use of system engineering tools, and collaboration with ransomware groups to conduct encryption operations and exfiltrate sensitive information. Notably, during the Israel-Hamas conflict between November 2023 and January 2024, Iranian-affiliated actors targeted Israeli-made programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and human-machine interfaces (HMIs), affecting sectors like water and wastewater, energy, food and beverage manufacturing, and healthcare in the U.S.
Business leaders are advised to prioritize cybersecurity by ensuring systems are updated, employing strong password policies, and implementing multifactor authentication. Regularly reviewing and securing internet-connected devices, especially those in operational technology environments, is crucial. Given the evolving threat landscape, organizations should stay informed through resources like CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog and collaborate with federal agencies to enhance their cyber defense strategies. Proactive measures are essential to safeguard against potential Iranian cyber activities that could impact operations and data integrity.
Source Materials: CISA Alert Joint Fact Sheet
Ransomware and Data Extortion Trends (June 24 – 30)
The Rundown
Between June 24 and 30, ransomware and data extortion activity declined, with 88 victim organizations reported across 17 leak sites, a 25% drop from the previous week’s count of 113. This decrease suggests a potential leveling in threat actor activity rather than a substantial reduction in attack volume.
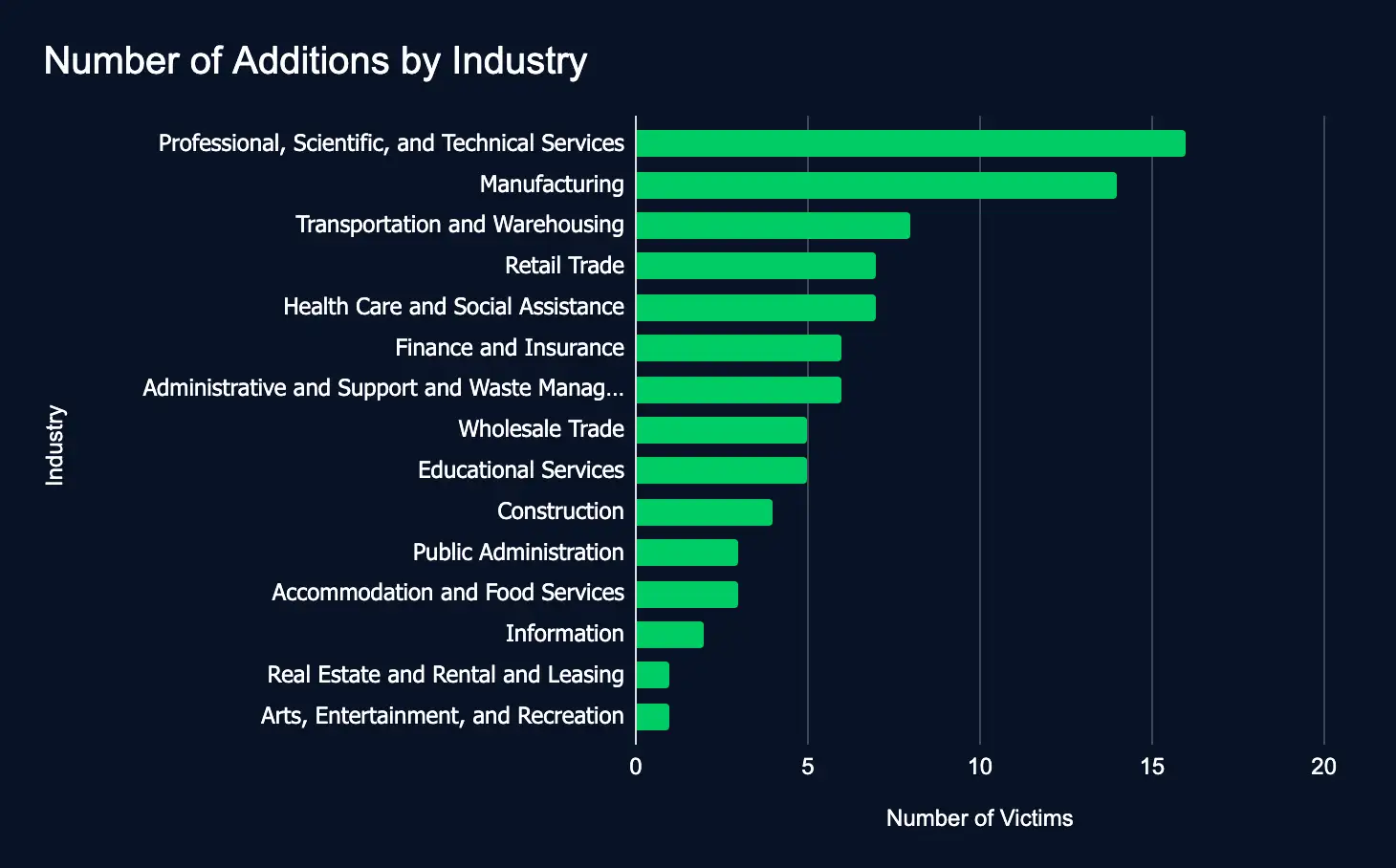
Professional Services, Manufacturing, and Transportation remained top targets, underscoring continued focus on high-value sectors. A significant portion of affected organizations were located in key regions, particularly the United States, Spain, Germany, and Canada, indicating a sustained emphasis on strategically important geographies.
For business leaders, these developments highlight the enduring and deliberate nature of ransomware threats. While weekly incident numbers may vary, the underlying risk to critical industries persists. Organizations should take this opportunity to reevaluate and reinforce their cybersecurity posture, ensuring their prevention, detection, and response capabilities are well aligned with today’s dynamic threat landscape.
Key Trends:
- Most affected industries:
- Professional, Scientific, and Technical Services
- Manufacturing
- Transportation and Warehousing
- Most affected countries:
- United States
- Spain
- Germany
- Canada
- Most active leak sites:
- Qilin
- Akira
- Play
Exploited Vulnerabilities in Citrix, TeleMessage, and Google Products Added to CISA’s Catalog – Immediate Mitigation Recommended
The Rundown
Between June 26 and July 2, CISA added three high severity vulnerabilities affecting products from Citrix, TeleMessage, and Google to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, signaling their active use in ongoing threat campaigns.
If left unpatched, these flaws pose a critical security risk, granting threat actors a potential foothold for initial access and broader system compromise. Given the extensive adoption of these technologies across sectors, the potential for operational disruption and reputational harm is substantial.
With heightened interest from both state-sponsored groups and financially driven adversaries, swift remediation is nonnegotiable. Any delay in response substantially increases the likelihood of exploitation and cascading consequences.
Citrix | NetScaler ADC and Gateway CVE-2025-6543
- Vulnerability Description: Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway contain a buffer overflow vulnerability leading to unintended control flow and Denial of Service. NetScaler must be configured as Gateway (VPN virtual server, ICA Proxy, CVPN, RDP Proxy) OR AAA virtual server.
- Exploited in a Ransomware attack? Unknown
- Action: Apply updates per vendor instructions.
- Date Added to catalog: 2025-06-30
- Recommended Mitigation Due Date: 2025-07-21
TeleMessage | TM SGNL CVE-2025-48928
- Vulnerability Description: TeleMessage TM SGNL contains an exposure of core dump file to an unauthorized control sphere Vulnerability. This vulnerability is based on a JSP application in which the heap content is roughly equivalent to a “core dump” in which a password previously sent over HTTP would be included in this dump.
- Exploited in a Ransomware attack? Unknown
- Action: Apply updates per vendor instructions. Media coverage.
- Date Added to catalog: 2025-07-01
- Recommended Mitigation Due Date: 2025-07-22
TeleMessage | TM SGNL CVE-2025-48927
- Vulnerability Description: TeleMessage TM SGNL contains an initialization of a resource with an insecure default vulnerability. This vulnerability relies on how the Spring Boot Actuator is configured with an exposed heap dump endpoint at a /heapdump URI.
- Exploited in a Ransomware attack? Unknown
- Action: Apply updates per vendor instructions. Media coverage.
- Date Added to catalog: 2025-07-01
- Recommended Mitigation Due Date: 2025-07-22
Google | Chromium V8 CVE-2025-6554
Vulnerability Description: Google Chromium V8 contains a type confusion vulnerability that could allow a remote attacker to perform arbitrary read/write via a crafted HTML page. This vulnerability could affect multiple web browsers that utilize Chromium, including, but not limited to, Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, and Opera.
- Exploited in a Ransomware attack? Unknown
- Action: Apply updates per vendor instructions.
- Date Added to catalog: 2025-07-02
- Recommended Mitigation Due Date: 2025-07-23
Recommendations
ATI recommends mitigative action occur according to the mitigation “Due Date” recommended by CISA.
Source: CISA
What We Mean When We Say
Estimates of Likelihood
We use probabilistic language to reflect the Intel Team’s estimates of the likelihood of developments or events because analytical judgments are not certain. Terms like “probably,” “likely,” “very likely,” and “almost certainly” denote a higher than even chance. The terms “unlikely” and “remote” imply that an event has a lower than even chance of occurring; they do not imply that it will not. Terms like “might” reflect situations where we are unable to assess the likelihood, usually due to a lack of relevant information, which is sketchy or fragmented. Terms like “we can’t dismiss,” “we can’t rule out,” and “we can’t discount” refer to an unlikely, improbable, or distant event with significant consequences.
Confidence in Assessments
Our assessments and projections are based on data that varies in scope, quality, and source. As a result, we assign our assessments high, moderate, or low levels of confidence, as follows:
High confidence indicates that our decisions are based on reliable information and/or that the nature of the problem allows us to make a sound decision. However, a “high confidence” judgment is not a fact or a guarantee, and it still carries the risk of being incorrect.
Moderate confidence denotes that the information is credible and plausible, but not of high enough quality or sufficiently corroborated to warrant a higher level of assurance.
Low confidence indicates that the information’s credibility and/or plausibility are in doubt, that the information is too fragmented or poorly corroborated to make solid analytic inferences, or that we have serious concerns or problems with the sources.
Share